|
| Cutaway and exterior views of target flowmeter |
Niagara Meters, based in Spartanburg, South Carolina, is a well recognized brand in the flow measurement field. For over a hundred and fifty years, their products have been used in a myriad of industries, including agriculture, petrochemical processing, and even aboard United States Navy ships. The company’s flow meter products target three basic functions: flow measurement of liquid, gas flowmeters, and flowmeters for steam. The three product application groups are anchored by Niagara’s operating technology thesis statement, “specializing in innovative, reliable products.”
The largest array of Niagara meters are those utilized for liquid flow measurement. For measuring liquid in an open channel, such as a weir or flume, Niagara offers an application specific ultrasonic open channel flowmeter, which comes equipped with one or more sensors, along with a level monitor. The device is flexibly configurable for different arrays, and calculates liquid level, open channel flow and differential level measurement.
 |
| Cutaway view of turbine flowmeter |
Measuring potable water flow through a pipe branch or system can be accomplished easily with the reliable mechanical MTX/WPX model series. In this turbine technology flowmeter, water pressure and resulting flow drives the internal turbine rotor. Magnetic coupling of the rotor to a flow indicator makes this instrument simple, reliable, and rugged for totalizing, rate of flow, and batch control applications.
Flow measurement in applications involving liquids with viscosity similar to oil are candidates for Niagara’s positive displacement oscillating piston flowmeter. This positive displacement device employs a piston which rotates in a flow chamber inside the meter. Liquid flow forces the piston to rotate, with the rotations recorded by a totalizer or pulse transmitter. Mechanical and smart electronic versions are available in a number of variants to meet the range of register and interface requirements.
Another mechanical positive displacement technology from the company uses a nutating disc and gear train to measure flow and provide a totalized flow register. The nutating disc is precisely fitted into the flow chamber and wobbles in a predictable manner that can be counted and used to measure volumetric flow. As with the oscillating piston products, a wide array of variants, including a smart meter version, are available to accommodate any register requirement.
Niagara also offers a fully electronic magnetic flowmeter, or Magmeter. The 6600 Series Magmeter can only be applied with conductive fluids, and converts the voltage produced when the fluid flows through a magnetic field to a volumetric flow signal for a high accuracy solution with no moving parts.
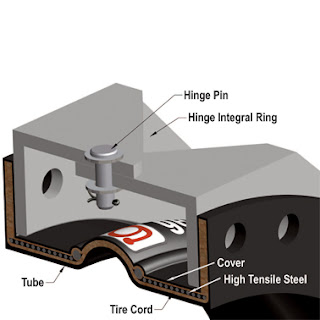
The company offers one additional category of flowmeter technology; applicable to liquids, gas, or steam. The target meter has a solid disk (the target) located in the flow path. The dynamic force of fluid movement acting on the target is converted to an electrical output signal that is proportional to flow rate.
All of Niagara’s flow measurement devices are time proven through many applications. For assistance in selecting and configuring a flowmeter for a particular application, share your requirements and process measurement challenges with a
product specialist. The combination of your process knowledge and their product application expertise will produce effective solutions.